Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs)
What are continuous glucose monitors?
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are small, wearable devices that continuously measure a person’s blood-glucose levels. They are largely used in place of glucose meters and finger sticks.
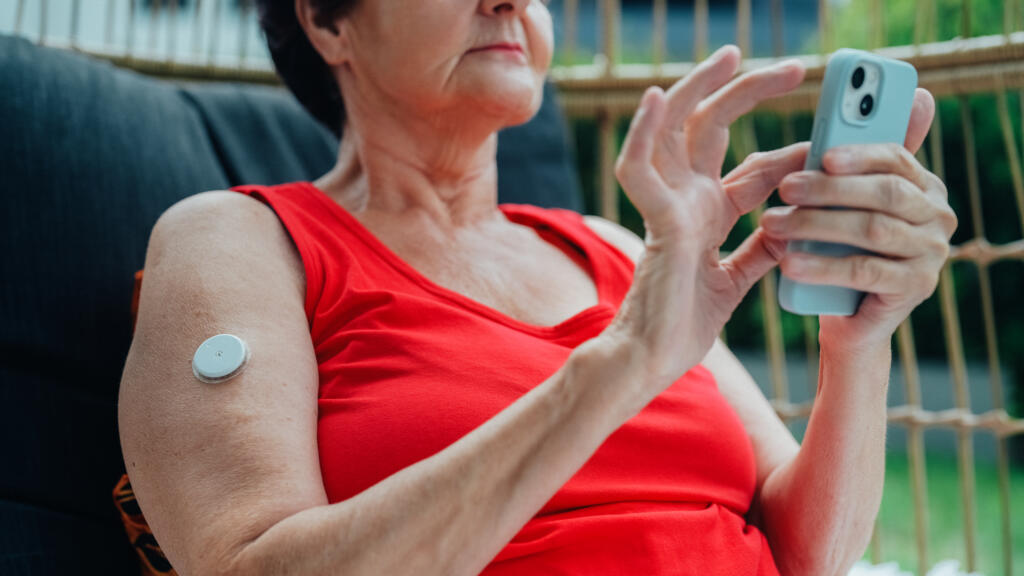
How do CGMs work?
A sensor just under the skin measures the glucose levels in real time. The levels are then relayed to a receiver, smartphone or watch, or insulin pump which displays the readings.
CGMs are mostly worn on the upper arm or abdomen, but some can be worn on other parts of the body.
Other things to consider about CGMs
- You need to wear the CGM all the time (24/7) to get the most benefit
- Glucose readings are available all the time—this can be overwhelming for some people
- They provide more glucose data to share with healthcare providers and family members
CGMs available in the U.S.*
The following are FDA-approved CGMs available for use in the U.S.
| Device name | More information |
|---|---|
| Abbott FreeStyle® Libre 2 Abbott FreeStyle® Libre 3 | https://www.freestyle.abbott/us-en/home.html |
| Dexcom G6® Dexcom G7® | https://www.dexcom.com |
| Medtronic Guardian™ Connect | https://www.medtronicdiabetes.com/products/guardian-connect-continuous-glucose-monitoring-system |
| Senseonics Eversense® E3 Senseonics Eversense® 365 | https://www.eversensecgm.com/ |
More T1D tech
Insulin pumps are small, wearable devices programmed with individualized settings to deliver insulin into the body. Combined with a CGM, they can also measure blood-glucose levels and adjust insulin dosage automatically.
Smart insulin pens and pen caps are used to track insulin doses for people who take multiple daily injections (MDI) of insulin.
Health Insurance Guide
If you think a CGM might be right for you, speak with your healthcare provider. Consult the Breakthrough T1D Health Insurance Guide to learn about insurance coverage for T1D management tools and therapies.